The Core of 5G, Network Slicing and Security
The release of Samsung’s Galaxy S10 allowed consumers to become more interested in 5G technology. In fact, 5G-related services have started competing for the first titles in the United States and other countries since 2018. However, the first service for customers was only launched via Samsung’s Galaxy S10 in April 2019, and after that, when Apple released a smartphone that supports 5G, it gained more than 10 million accumulated users in December 2020, and 5G technology is gradually expanding its influence on people’s daily lives.
What is 5G?
In order for us to understand what 5G technology is, it’s important to exactly know the differences between 4G and legacy mobile communication networks.
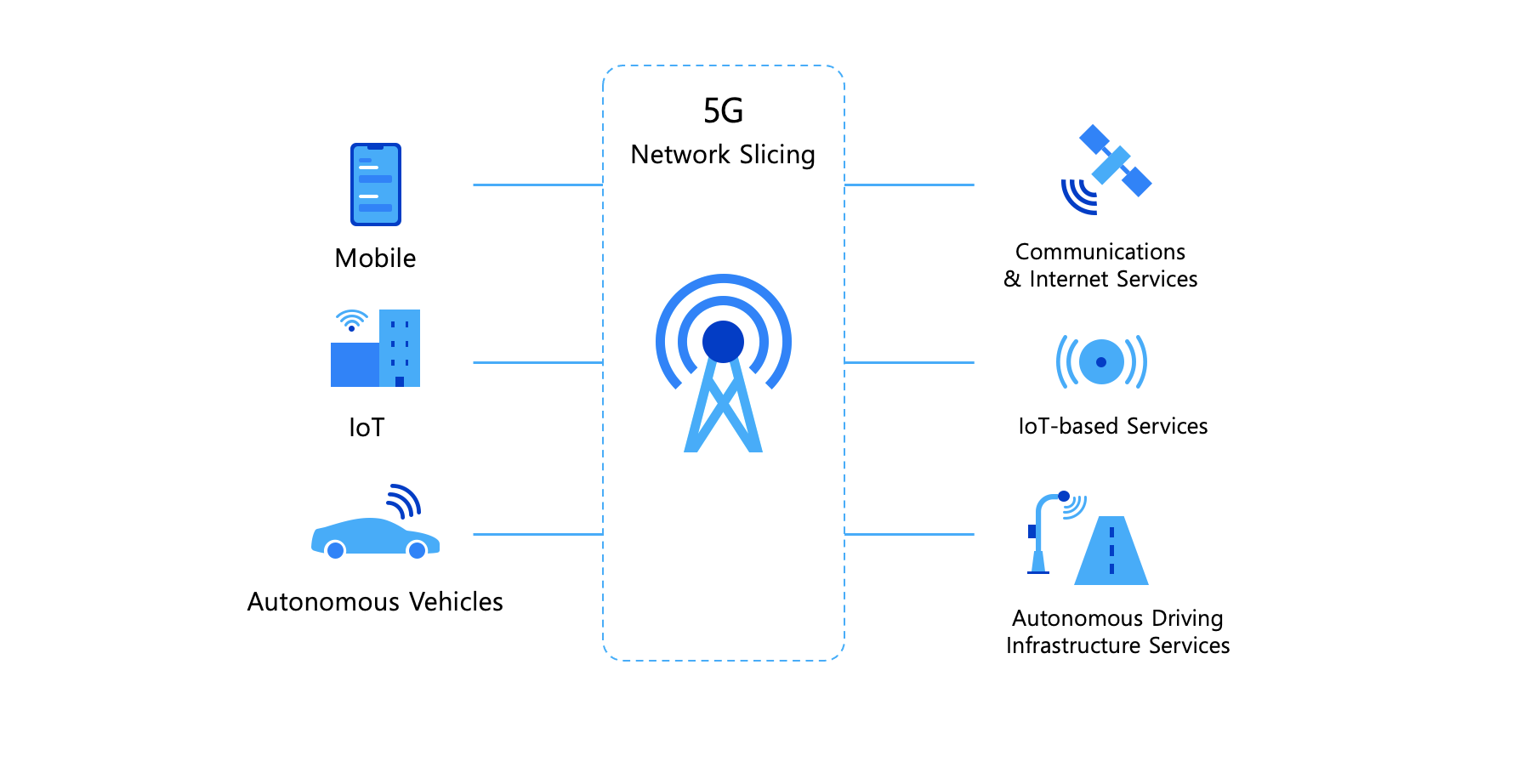
The main difference from 4G is the ‘network slicing’ technology. Network slicing technology is a technology that allows one physical network to be divided into multiple logical networks to provide services. It is a technology that can greatly increase the efficiency of network operation.
On the other hand, 4G is characterized by relatively inferior network operation efficiency as it can only provide a single service to a single network. The reason why you can expect to enjoy various services such as autonomous driving and deployments in smart cities that use the 5G technology is basically all about using the network slicing technology.
5G has the features we are familiar with: ultra-fast, hyper-connected, and ultra-low latency features. In fact, these features are relative concepts, but there are also technologies that can only be implemented in a 5G deployed environment, based on these three features.
1) Ultra-High-Speed
5G’s ultra-high-speed features enable large-capacity communication without any time constraints. Compared to 4G, it can maintain a transmission speed of up to 20 Gbps, which is about 20 times faster than 4G. Thanks to the feature that can quickly accommodate large amounts of traffic, it is possible to stream 4K and 8K videos in real-time and implement technologies that require large capacities such as holograms, AR, and VR.
2) Ultra-Low Latency
The transmission delay of 5G is about 1ms (0.001 seconds), which is 1/10 compared to 4G. Thanks to this, 5G has become an integral part of autonomous vehicle technology, which must constantly communicate with the network from one move to another. Other technologies such as factory automation systems and telemedicine can also be supported by 5G technology.
3) Ultra Connection
Also called mass-connect communication, this feature can be measured as an indicator of the number of connectable devices per area. 5G can connect 1 million devices per 1 km square, more than 10 times that of 4G. With this, when a large number of IoT devices such as smart cities, smart buildings, and smart logistics where a certain area or network connection is required, the feature of hyper-connection can be utilized.
Why We Need 5G Security
As mobile communication technology advances to the next generation, it makes it almost impossible for us to be less exposed to various security threats and vulnerabilities than now. Therefore, the successful employment of new mobile communication technologies will only work depending on how well we understand the vulnerabilities and prepare to protect against them in advance. This is why we need to consider the security of 5G as it’s getting a step closer to the commercialization stage.
In fact, there are many examples that show that security vulnerabilities in mobile communications can cause catastrophic damage. In February 2020, with only 99 smartphones in Germany, hackers were able to manipulate Google Maps to make normal roads look like they were congested. A vulnerability was discovered that could allow a fake base station to send fake emergency disaster updates to users’ devices through mobile network hacking.
In order to fully understand the security required for 5G deployment, we need to pay attention to the aforementioned network slicing technology. In a 5G environment, various services communicate through a virtual network that is “sliced”. In other words, while previous mobile communication networks had a closed structure, 5G provides an open mobile communication network with a distributed structure. Therefore, since multiple sliced virtual networks were actually one single network, to begin with, they may be considered vulnerable to hacking and become attempting targets – because even if hackers attack one device, they can gain access to multiple services and data.
In particular, if a single network is divided into services such as autonomous driving, remote medical services, and IoT, this means that security around the 5G network is an important factor because these services can be seen much more vulnerable and risky when attacks have occurred.
Last year, the U.S. government criticized and banned Huawei’s 5G equipment because of its security-related vulnerabilities. In short, if Huawei’s 5G network were to be installed across the United States, one single attack may be able to exploit the data that could threaten national security.
As the spread of 5G expands, competition for leadership in 5G networks is intensifying. The United States is constantly pursuing a system to protect the 5G network technology and has established strategies to prevent certain countries from expanding their 5G infrastructures. In the midst of an invisible war over 5G, ‘cybersecurity’ is again appealing itself as a key factor in establishing the entire 5G network environment.
As mentioned earlier, emerging technologies and services can be created via autonomous driving technology, cloud services, edge computing, and authentication security. Penta Security develops and provides security solutions optimized for 5G environments and plans to contribute to a safe 5G environment based on existing web firewall and authentication security technologies, cloud security, and IoT security solutions. For more information on Penta Security’s security solutions, please visit the website.
Check out Penta Security’s product lines:
Web Application Firewall: WAPPLES
Database Encryption: D’Amo
Identity and Access Management: ISign+
Car, Energy, Factory, City Solutions: Penta IoT Security
