COVID-19 and Its Effects on Cybersecurity
2020 was associated with many things, the global COVID-19 pandemic being one of them. The effects of this pandemic were felt around the world in basically every industry. As more and more industries and society as a general began to operate online, we saw a rise in traffic online and with the integration of different applications, we also saw an increase in the potential for threats and attacks. The need for cybersecurity remains greater than ever as COVID-19 has brought about new changes and challenges for many. Here are some of the ways the pandemic has affected security, and what we can do about it in 2021.
1) Pandemic Phishing
Although phishing is hardly new, it moved to a wider range of platforms last year. A channel that’s known for going “viral,” social media was often used to scam unsuspecting users of their money or their information.
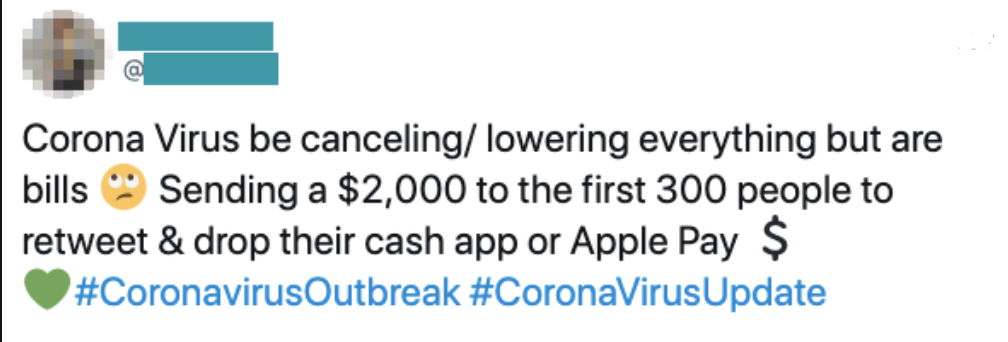
With the global pandemic, many people, unfortunately, were in financial need due to unemployment or rising costs of living or medical care. In hard times, people are often much more likely to let their guard down, and unfortunately, malicious actors will swoop in to take advantage of their trust.
2) The Rise of Zero Trust
Because of the increase in these types of scams, we also saw a rise in many companies and cybersecurity firms pushing for a “Zero Trust” cybersecurity policy. Rather than the more traditional “perimeter-based” model where all inside a certain network are trusted, the Zero Trust model looks to authentication and authorization of every individual, asset, device, and application going in and out of the network.
Although it may seem more cumbersome, it decreases the risk of potential threat and actually provides more freedom of access. Organizations can assume that nothing is secure, and ensure that only certain devices can access their corporate servers. Therefore, even if certain users are outside of their usual network, they can still securely access their corporate resources because they go through proper verification processes.
3) Cybersecurity for a Remote Workforce
Zero Trust becomes even more important as more and more companies are promoting remote work. While work-from-home (WFH) structures were often seen as a luxury that very few companies offered, with the pandemic we have seen a rise in the number of employees utilizing remote resources to complete their workloads, and it doesn’t seem like it will be going away anytime soon.
This means that cybersecurity is even more important, as employees may be utilizing non-secure Wi-Fi networks from public spaces in order to connect to company information systems. Organizations can oversee this by having employees exclusively use a VPN when working remotely so that all traffic is encrypted. Other security measures like Two-Factor Authentication (2FA) or firewalls can be utilized in order to verify traffic.
4) Healthcare Cyber Attacks
The healthcare industry was hit hard with the global pandemic, with many countries and states running out of ICU beds, PPE, and other essential equipment. However, those were not the only commodities that were vulnerable. Many healthcare providers or related companies were flooded with data breaches, with hackers preying on a vulnerable time. With frontline workers already inundated with patients and testing, it was most definitely not an ideal time to be dealing with ransomware or DDoS attacks.
Unfortunately, it doesn’t look as though 2021 will be much better; as the vaccine rollout is underway in many countries, this provides even more data for malicious actors to mess with. The European Medicines Agency (EMA) already announced that they had been targeted in a cyberattack, where papers relating to the new Pfizer vaccine were reportedly targeted. Medical technology has been evolving in order to be more efficient and smart, connecting to networks to be part of a medical IoT — but with more and more lives at stake, especially due to COVID-19, there’s no time like the present for implementing tighter security measures.
While we all desire to go back to “normalcy,” it’s likely that this pandemic has changed many and their industries. It has most definitely changed the way that many organizations structure their cybersecurity management systems. Authentication and encryption are more important now than ever, and remote security tools will remain a top priority as WFH will become a staple of many company departments.
For more information about remote security, head to Remote Access Solution (RAS) by Cloudbric, which employs 24/7 traffic monitoring through encrypted channels to block out web-based malicious activities from your network.
Check out Penta Security’s product lines:
Web Application Firewall: WAPPLES
Database Encryption: D’Amo
Identity and Access Management: ISign+
Car, Energy, Factory, City Solutions: Penta IoT Security