Security Strategy for Metaverse Platforms
As the virtual environment becomes more common for business environments, metaverse platforms are spreading across different industries. Metaverse is a new word that combines meta (meaning transcendence) and the universe, which refers to a three-dimensional virtual world.
Users can expand their real-world by creating their avatar through the platform. For example, the metaverse platform ‘ZEPETO’ created by Naver has already exceeded 200 million users and on ‘Roblox’, the infamous metaverse game was valued at over 34 billion dollars on the first day of trading after the IPO. With the prospect
With the prospect that the size of the metaverse market will exceed several billion dollars, many governments around the globe are looking into investing further in these platforms. So, what are the major strengths of Metaverse?
Metaverse to Increase Efficiency and Reduce Costs
As the real and virtual spaces begin to interact and influence each other due to the pandemic, the metaverse is now being evaluated as a world where new industrial, social, and cultural values are created. Metaverse users actively utilize the digital space to reveal and communicate their different identities that are different from reality.
Metaverse can save time and costs. Since everything takes place in the virtual space, the hardware and software costs generated in the physical space can be greatly reduced. In the case of SMEs, you can build and use your training institute and even virtual offices in the metaverse.
In addition, the socially distanced environment can be more efficient through the metaverse. On the platforms, avatars and actual video chat features can be used simultaneously, and users can even share data whilst on video calls.
For example, if you create a virtual training center with the metaverse platform ‘Gather Town’, you can train your employees through data sharing, team learning, presentations, and discussions organized by all participants. Various communication methods of metaverse can allow users to express their opinions as avatars, so it makes things easier for people to express themselves freely.
Metaverse is Not Just a Virtual Space
In the metaverse, contents, services, and products are digitally supplied, and consumers purchase and use them through various methods. In other words, transactions that occur in a virtual space directly affects capital in the real world. This means that cyberattacks targeting products in the virtual space within the metaverse can end up causing damage to the real world.
As a matter of fact, according to Perkins Coie LLP’s <2020 Augmented and Virtual Reality Survey Report>, the top priority for the metaverse implementation technology and content development industry in terms of legal risk is customer privacy and data protection, not product/service quality assurance (Production Liability).
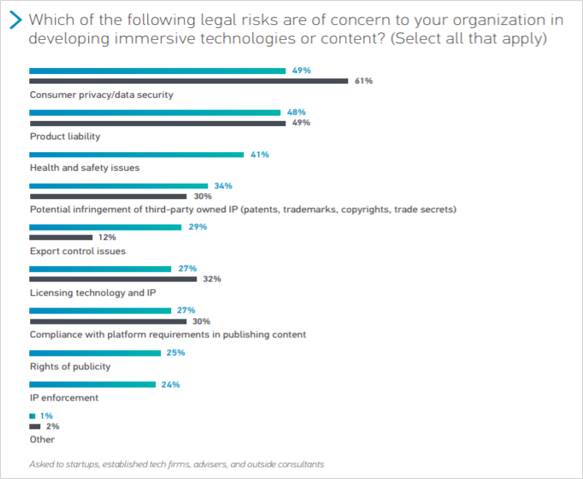
This means that at the end of the day when encountering a new virtual space such as the metaverse, the fear of not knowing what will happen is greater than the potential damages that can be caused by any sort of malfunctioning. In fact, on the metaverse, various privacy violations such as exposure of the users’ real identity or account hijacking can also happen, just like in the real world.
Complex services on the metaverse platform generate new types of personal data such as user consumption habits, location information, and biometric information. Because such personal data is generated and shared in real-time, it is complicated to determine exactly what personal data is shared, with whom, for what purpose, and when it is destroyed. This makes it difficult to exercise control over your personal information.
Data Security Tailored to the Metaverse Through Required Privacy Security Policy
Metaverse, like other IT service platforms, has data and privacy security issues. However, in addition to the existing information security measures, it is necessary to establish a customized strategy considering the characteristics of the metaverse.
For example, since the data of users of the Metaverse platform is located on different servers around the world, it is not only necessary to discuss how to handle different personal data processing guidelines in each country, but also to protect the avatar in the metaverse as a person, considering them as individual information subjects.
As it is an emerging platform, excessive regulation can hinder the development of the industry, therefore, institutional devices for user protection must be prepared along with the metaverse industry promotion policy.
