The Future of Autonomous Ships Explained
Have you seen the movie Titanic? RMS (Royal Mail Ship) Titanic, a British luxury liner that sank in the North Atlantic Ocean on 12th (to 15th) of April back in 1912, was en route to New York City from Southampton, England with more than 2,200 passengers and crew aboard. It is estimated that more than 1,500 died, making the sinking one of the deadliest marine disasters. With a slight exaggeration, marine disasters like Titanic would never happen again with autonomous ships.
What is an Autonomous Ship?
An autonomous ship (or autonomous cargo, container, surface ships) are seaborne vessels that transport over navigable waters with little or no human interactions. They are highly dependent on computers and other robotic equipment just like autonomous vehicles which however could exacerbate the consequences of cyberattacks. As they’re approaching reality, performing safety measures (including verification, etc.) has become one of the main concerns. Let’s first take a look at the differences between the types of autonomous ships below.
-
Types of Autonomous Ships
Just like autonomous vehicles (smart cars, connected cars, connected vehicles), autonomous ships also have different names depending on the function or purpose of use. IMO (International Maritime Organization) establishes international standards for maritime transportation, and stipulates maritime autonomous surface ships (MASS) as ships that can operate without any human interaction. In other words, it’s also called an unmanned surface vehicle (USV), which basically means that it runs on water or a smart ship, meaning it’s smart enough to sail on its own.
-
Levels of Autonomy
Autonomous ships also have their own level of autonomy just like autonomous vehicles. According to IMO, it can be explained in four stages where the ship supports decision-making (level 1) to an extent where they allow full autonomous operation without any human control (level 4).
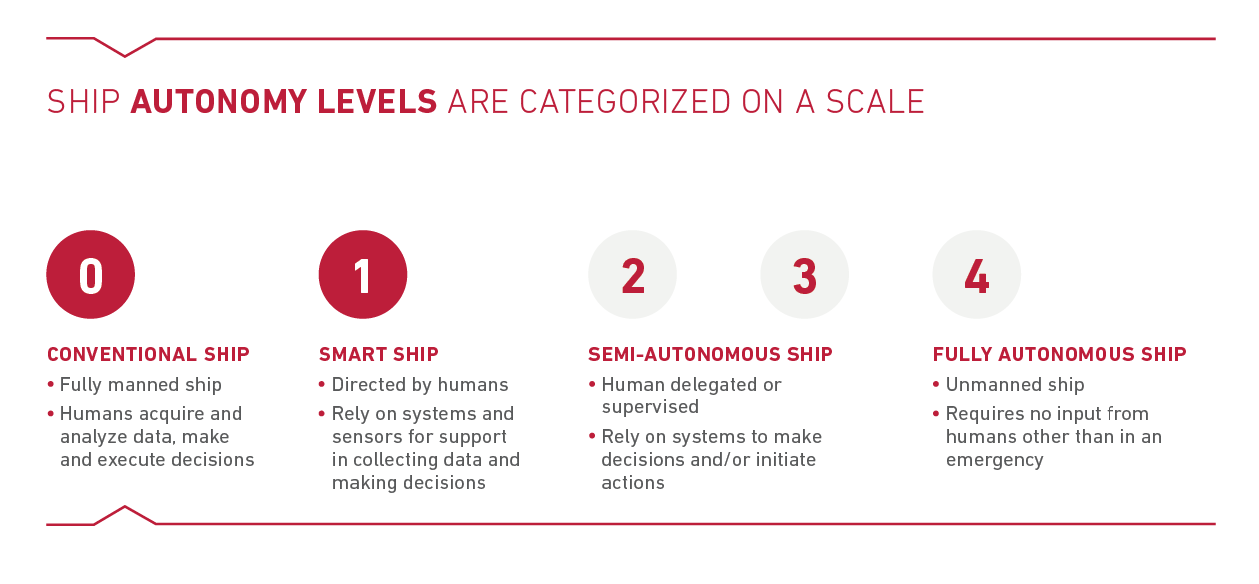 Source: Marine & Offshore Bureau Veritas
Source: Marine & Offshore Bureau Veritas
-
Security
As technology becomes more and more advanced, one of the factors that attract our attention is security. In order for an autonomous vehicle to drive on the road on its own, it must be ‘connected’ to a real-time communication system between each vehicle, traffic lights, and roads. This principle applies equally to the ships out there in the sea. The self-driving vessel is to detect and connect with the conditions of the waves, weather, and the location and route of nearby ships. Therefore, in order for this to work, security must be applied at the point of connection.
With the development of self-driving vessels in earnest, Penta Security has successfully concluded a business agreement for joint research on autonomous ship security solutions with the Korean Register of Shipping, an international shipping inspection agency last year. We will cooperate in areas including risk analysis of autonomous ships, safety evaluation, and verification of cybersecurity solutions required for autonomous ships.
The Benefits
The biggest advantage of self-driving vessels is that they can significantly reduce the cost of managing incurred during operation since manpower and fuel costs account for more than 80% of the operation costs. This commercialization will reduce the number of people on the ship and increase the efficiency of space as well as fuel efficiency.

Source: Rolls-Royce
As a part of the New Deals, many governments have shown their interest and support in the development of autonomous vehicles and ships. Steps have been taken to further develop the existing powerhouse and the Ministry of Trade, Industry, and Energy along with the Ministry of Maritime Affairs and Fisheries have also set up a business group for the development of self-driving vessels. The ministries will invest more than 13 billion dollars for the next 6 years until 2025 and some projects have already begun starting this July.
In addition to technology development, we will be able to define autonomous ships through the roadmap for the regulation revolution and prepare related systems and standards such as autonomous manpower and cybersecurity in the near future. In the absence of globally harmonized standards, this process will serve as an opportunity for Penta Security to take part in the standardization of the global market with leading government projects.
